Oxygen Level, Pulse Oximeter, Hypoxemia And COVID-19 Malaysia Leave a comment
In 2022, Malaysia will enter its third year with COVID‐19, the coronavirus disease caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2).
Since the first COVID-19 case was detected on 25 January 2020 in Malaysia, the COVID-19 pandemic has enormously affected the daily life of people around Malaysia.
With a surge in cases thereafter, our government has taken various kinds of actions to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
The actions to curb the spread of the disease, including:
- Physical distancing rules
- Restrictions on social gatherings
- Appropriate use of face mask
- Movement Control Order (MCO)
- Conditional Movement Control Order (CMCO)
- Extended movement control order
- Border closures

Nowadays, we can also protect ourselves by monitoring signs and symptoms of COVID-19 with various kinds of devices available in the market.
While we may be able to identify the more common symptoms of COVID-19, it has been reported that sometimes oxygen levels may start to drop even before any symptoms appear.
In such cases, we can use devices such as pulse oximeters to track oxygen levels and detect cases of “silent pneumonia”, one of the most serious consequences of COVID-19.
In this article, I will talk about the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and how we able to monitor symptoms of low oxygen levels while being in home.
Here are the topics that will be covered in this article; you can click on the red color text to view your favorite topic instantly:
- COVID-19 Signs And Symptoms
- How Does COVID-19 Lower The Body’s Oxygen Levels?
- Oxygen Saturation In Human Body
- What Is A Pulse Oximeter
- Purpose And Uses Of Pulse Oximeter
- How To Use A Pulse Oximeter At Home
- Pulse Oximeter : What Is Low And Normal Oxygen Level?
- Low Blood Oxygen Levels Signs And Symptoms
- Hypoxemia, Hypoxia And Hyperoxia : Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
- How To Use An Oxygen Concentrator Correctly?
- Oxygen Level, Pulse Oximeter, Hypoxemia, And COVID-19 Malaysia Conclusion
COVID-19 Signs And Symptoms
According to World Health Organization ( WHO ) COVID-19 can affect different people in different ways; patient may show signs and symptoms as state as below.
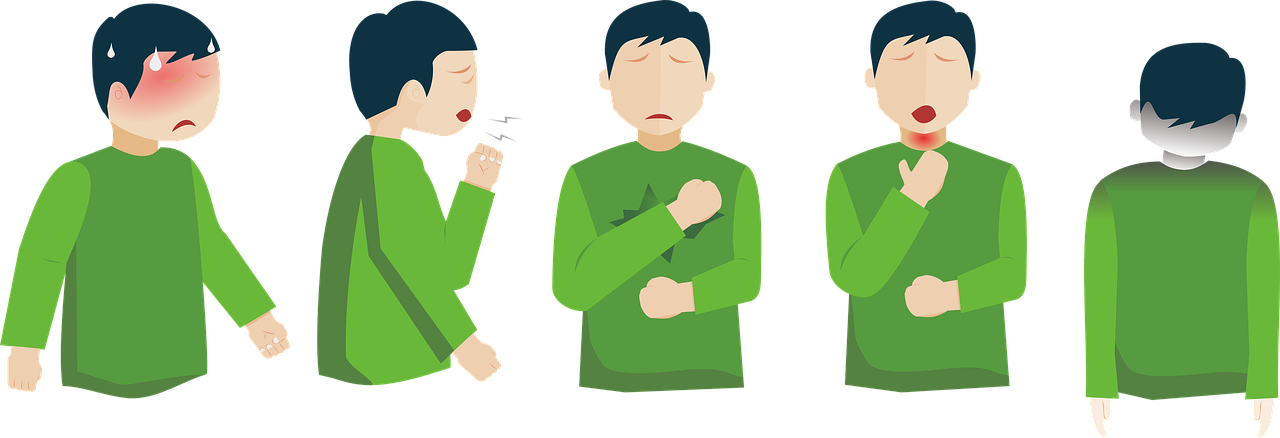

Most common symptoms:
- Fever
- Cough
- Tiredness
- Loss of taste or smell.
Less common symptoms:
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Aches and pains
- Diarrhoea
- A rash on skin, or discolouration of fingers or toes
- Red or irritated eyes.
Serious symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Loss of speech or mobility, or confusion
- Chest pain.
How Does COVID-19 Lower The Body’s Oxygen Levels?
As we know COVID-19 is a respiratory illness.
If we’ve been exposed to coronavirus, the virus enters our body through the respiratory system.
Next, it will start causing direct injury to the lungs via inflammation and pneumonia.
This will have a negative impact on how well oxygen is transferred into the bloodstream of our body.
As a result may lower your blood oxygen levels at some point in time.
When our bodies do not receive enough oxygen to perform normal bodily functions, our body parts and organs will start to fail and collapse.
This is why COVID-19 may become fatal, if not received treatment in time.
Devices like pulse oximeters are suitable for someone experiencing COVID-19 signs and symptoms to make sure the blood is well oxygenated.

At PL Science Medic, we provide Andon Pulse Oximeter, one of the best pulse oximeter Malaysia for medical professionals to use for monitor the health of people with conditions that affect blood oxygen levels.
- High Accuracy
- Low Power Consumption
- Auto-rotate screen
- Color Display
Oxygen Saturation In Human Body
Red blood cells actually act like couriers in our bodies.
Each of the cells can pick up to four oxygen molecules in our lung.
Then, transport it across the body, getting them to various kind of organs, tissues such as heart and brain.
Our body’s vital systems need a normal percentage of oxygen inside the blood at all times, known as oxygen saturation, also known as “O2 sats”.
However, sometimes our blood can get either too much or too little oxygen.
In these cases, there can be serious health consequences.
In the case that we get too much oxygen can cause hyperoxia.
Hyperoxia occurs when cells, tissues and organs are exposed to an excess supply of oxygen (O2) or higher than normal partial pressure of oxygen.
On the other hand, if the blood gets too little oxygen, it can cause hypoxemia, which occurs when levels of oxygen in the blood are lower than normal.
Oxygen saturation is usually measured one of two ways: arterial blood gas test (ABG or Sa02) and pulse oximetry (Sp02).
ABG is usually only done in a hospital setting, while pulse oximetry is done in a variety of healthcare settings, including your medical professional’s office with a device such as a pulse oximeter.
ABG
An ABG value refers to the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood running through your veins.
If you wish to perform ABG test, you need to go to hospital.
The nurse or lab technician will draw blood from your artery, such as the radial artery in the wrist or the femoral artery in the groin.
Your blood sample will be analyzed by a machine or in the lab.
Your ABG value gives medical professionals a sense of how efficiently your hemoglobin exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Pulse Oximetry
A pulse oximetry reading reflects the percentage of oxygen found in arterial blood.
If you wish to perform pulse oximetry tests, you can use a pulse oximeter to read wavelengths reflected from your blood.
Unlike ABG test, pulse oximetry is non-invasive.
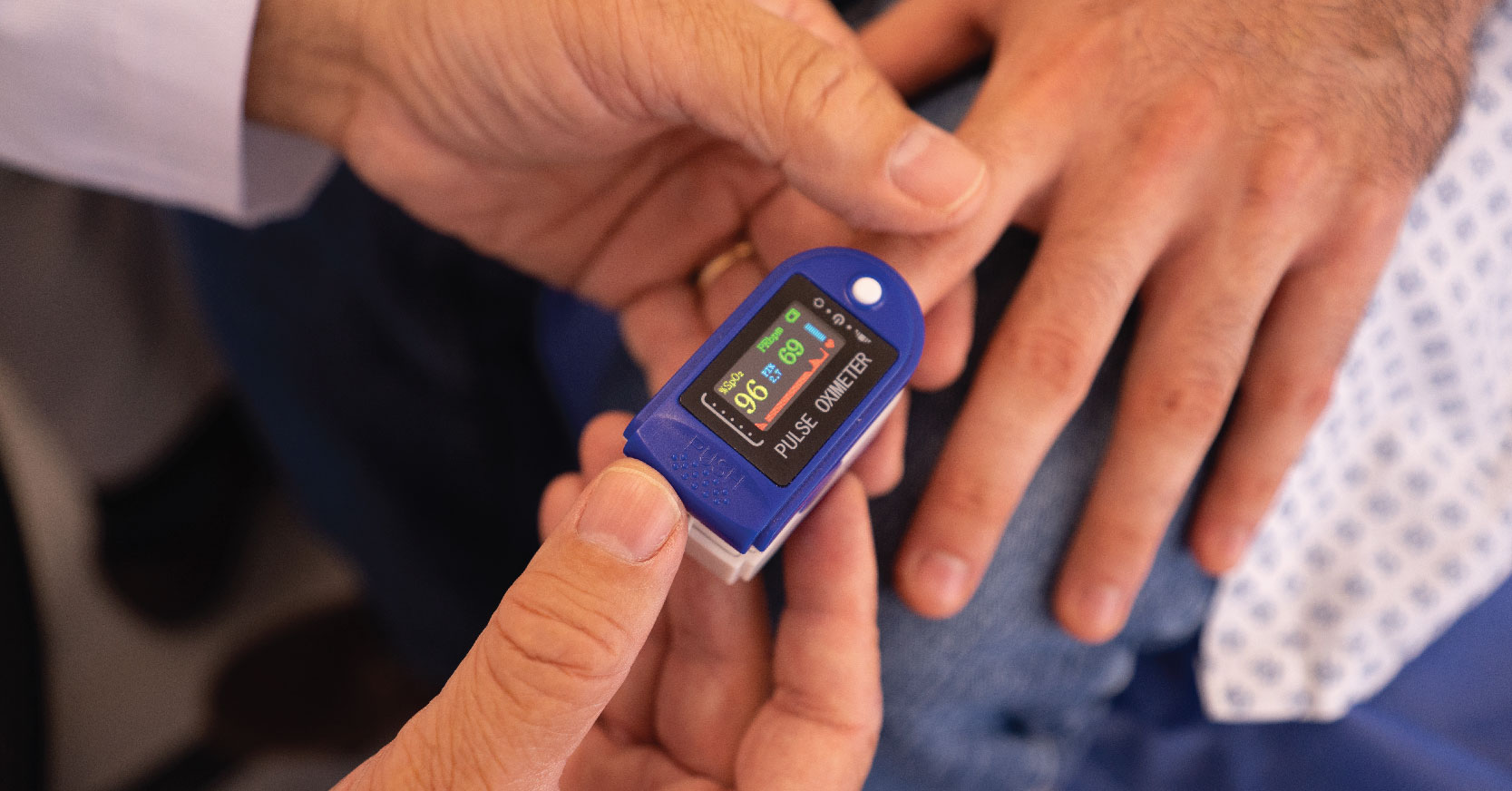
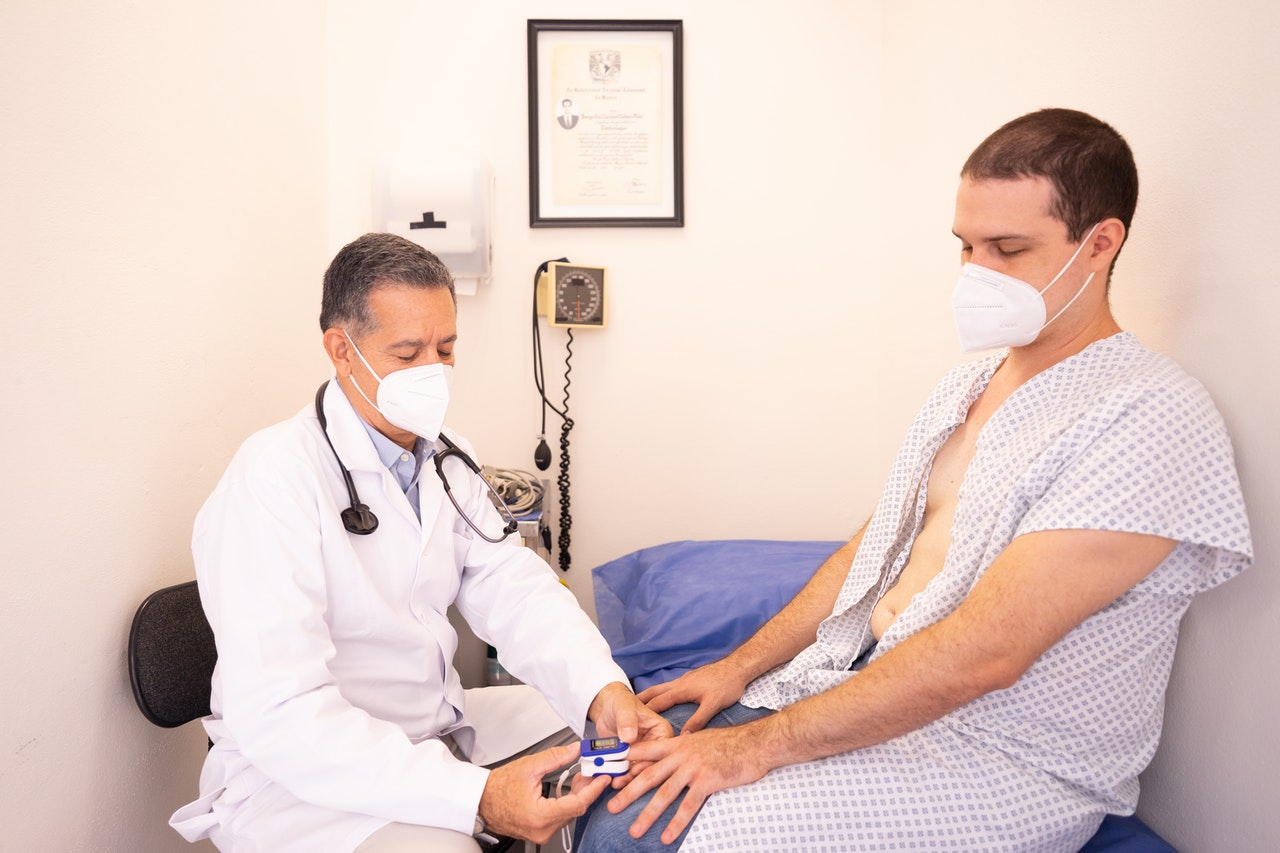
The pulse oximeter is simply attached to your finger and the results will appear on the device screen after a while.

With this device, you can monitor their oxygen saturation levels easily.
Nowadays, we are able to purchase high quality pulse oximeter Malaysia easily at professional medical device provider shop or online shop.
What Is A Pulse Oximeter?
Maybe you are still wondering what pulse oximeters are, do we really need it?
So let us take a deeper look at pulse oximeters.
As mentioned before, a pulse oximeter is a device used to perform pulse oximetry tests.
The test was an easy, painless and reliable measure of how well oxygen is being sent to parts of your body furthest from your heart, such as the arms and legs.
A pulse oximeter is a tiny clip-like device that usually clips over your fingertip or clips on your ear lobe.
The pulse oximeter uses light beams to measure the oxygen saturation of the blood and the pulse rate.
It reports blood oxygen levels via an oxygen saturation measurement called peripheral capillary oxygen saturation, or SpO2.
Purpose And Uses Of Pulse Oximeter
Next, let’s take a look at the purpose and uses of pulse oximeters.
The purpose of pulse oximetry is to see if your blood is well oxygenated.
This information helps medical professionals monitor the health of people with conditions that affect blood oxygen levels and decide if they need extra oxygen.
In the past, pulse oximeters were used in medical professional’s offices and hospitals.
But nowadays medical professionals may think it’s a good idea for some people to use one at home.
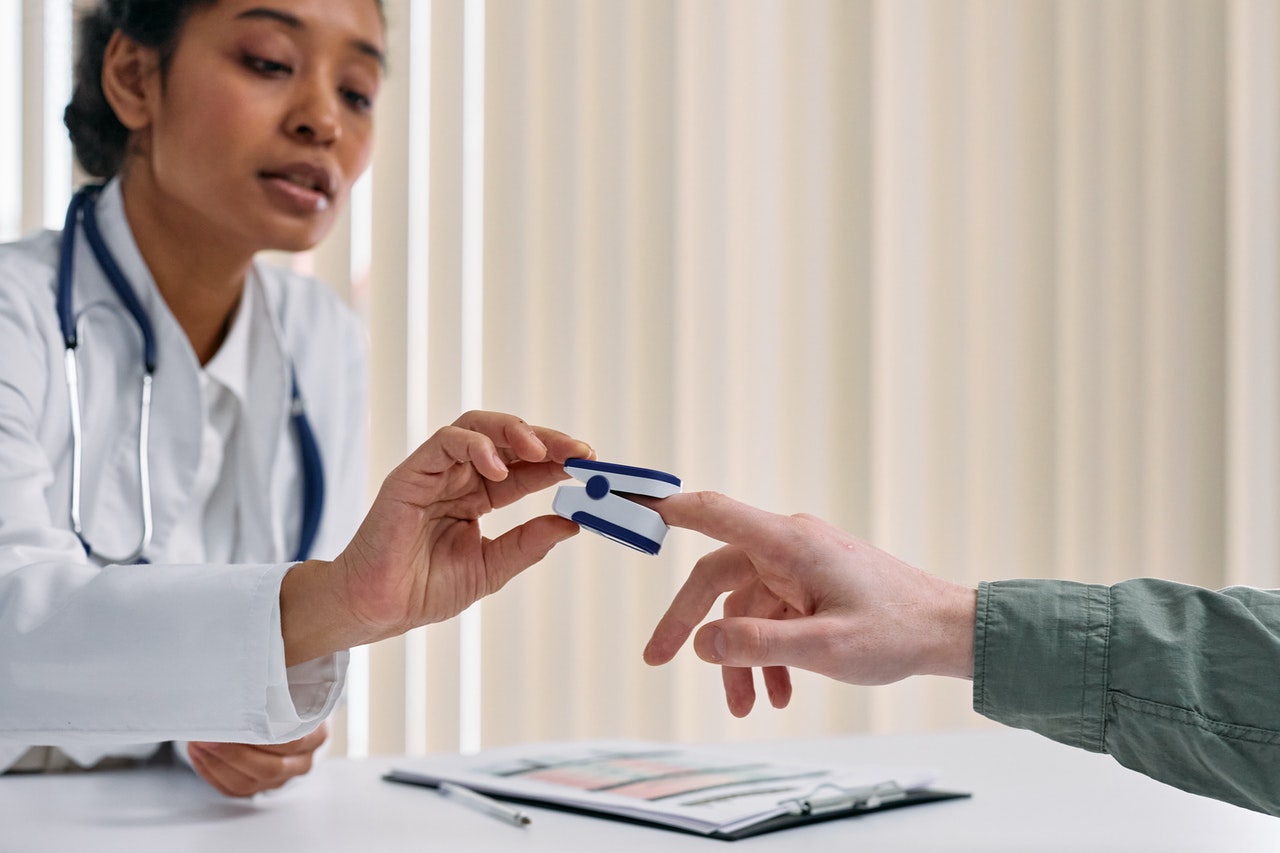

This may include people who have a condition that affects their oxygen levels.
Examples include people who have long-term heart or lung problems or an infection like COVID-19.
These also can include:
- Lung cancer
- Anemia
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Pneumonia
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Congenital heart disease
Doctors and medical professionals also use pulse oximetry for a number of different reasons, including:
- To assess how well a new lung medication is working
- To judge how helpful a ventilator is
- Monitor oxygen levels during or after surgical procedures
- Determine if patient requires supplemental oxygen therapy
- Determine how effective supplemental oxygen therapy is
- To assess someone’s ability to tolerate increased physical activity
- To evaluate whether someone momentarily stops breathing while sleeping like in cases of sleep apnea
Usually a low blood oxygen level causes symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath.
We will take about low blood oxygen levels later in this article.
In the case of being infected by COVID-19, you may not have symptoms from a low oxygen level.
Your doctor may suggest checking your oxygen level at home with a pulse oximeter.
This can help you know if your oxygen level is dropping and if it requires medical attention, even if you don’t have symptoms.
How To Use A Pulse Oximeter At Home?
Before using a pulse oximeter, it is important to follow medical professionals recommendations about when and how often to check your oxygen levels.
You also need to be aware that multiple factors can affect the accuracy of a pulse oximeter reading.
The factors that can affect the accuracy of a pulse oximeter reading include:
- Poor circulation
- Skin pigmentation
- Skin thickness
- Current tobacco use
- Temperature of skin
- Use of fingernail polish.
- Children ages 0 – 12 years old may require a different pulse oximeter probe.
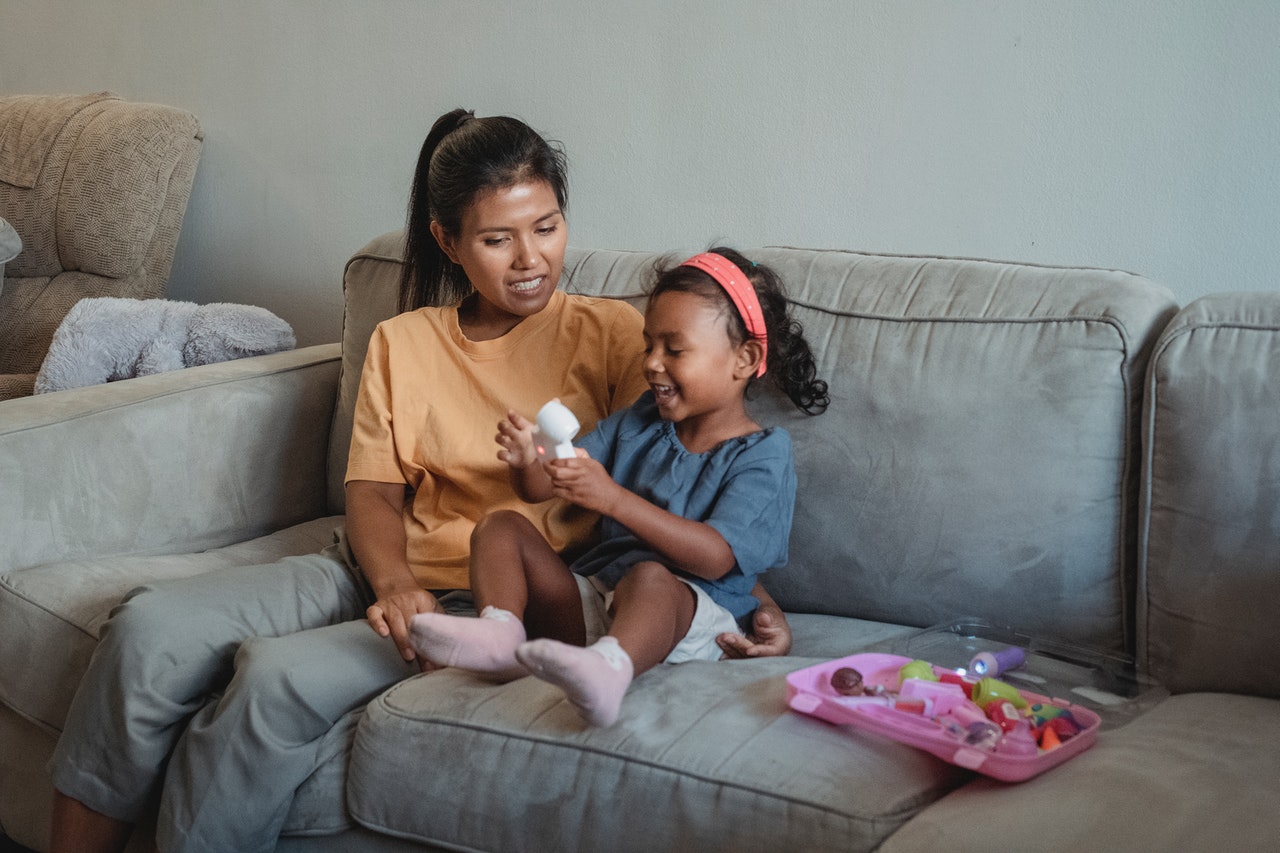

To get the best reading from a pulse oximeter, you need to:
- Follow the pulse oximeter manufacturer’s instructions for use.
- When placing the oximeter on your finger, make sure your hand is warm, relaxed, and held below the level of your heart.
- Preferably sit still and do not move the part of your body where the pulse oximeter is located.
- Make sure the light source in the pulse oximeter is not blocked by dust and dirt
- Avoid taking the reading under a direct bright light source.
- Bodily functions such as shivering or cold extremities can alter the readings so beware of it.
- Do not press the pulse oximeter while the reading is being taken
- Wait for a few minutes until the reading stops changing and displays one steady number.
- Write down your oxygen levels with the date and time so you can easily track changes and report these to your health care provider.
- You can remove the device once the testing is over.
Pulse Oximeter : What Is Low And Normal Oxygen Level?
Most of the pulse oximeters in the market show two or three value.
The most important number, oxygen saturation level, is usually abbreviated SpO2, and is presented as a percentage.
The pulse rate (similar to heart rate) is abbreviated PR.
Usually oxygen saturation values are between 95% and 100% for most healthy individuals.
However, oxygen saturation sometimes can be lower in people with lung problems.

Oxygen saturation levels are also generally slightly lower for those living at higher altitudes.
Normal Blood Oxygen Levels
A normal blood oxygen saturation rate is often considered between 95% and 100%.
However, you may not experience any symptoms yet before the percentage is lower.
Blood Oxygen Levels Need to Be Concerning
Oxygen concentrations between 91% and 95% may indicate a medical problem.
You should contact medical professionals if you are in this situation.
Low Blood Oxygen Levels
The medical definition of a low blood oxygen rate is any percentage below 90% oxygen saturation.
Oxygen saturation below 90% is very concerning and indicates an emergency.
If you experience low blood oxygen level, you need to seek emergency medical attention.
When Will Low Oxygen Saturation Start To Affects The Brain
Eventually, if oxygen saturation has fallen to between 80% and 85%, the brain may be affected by the lack of oxygen.
Syndromes such as vision disorders may start to occur.
Blue Discoloration Of The Skin Or Lips : Cyanosis
Cyanosis is one of the visible symptoms of low blood oxygen levels.
It will cause a blue tinge to develop on the skin, particularly around the mouth, lips, and beneath the fingernail matrix.
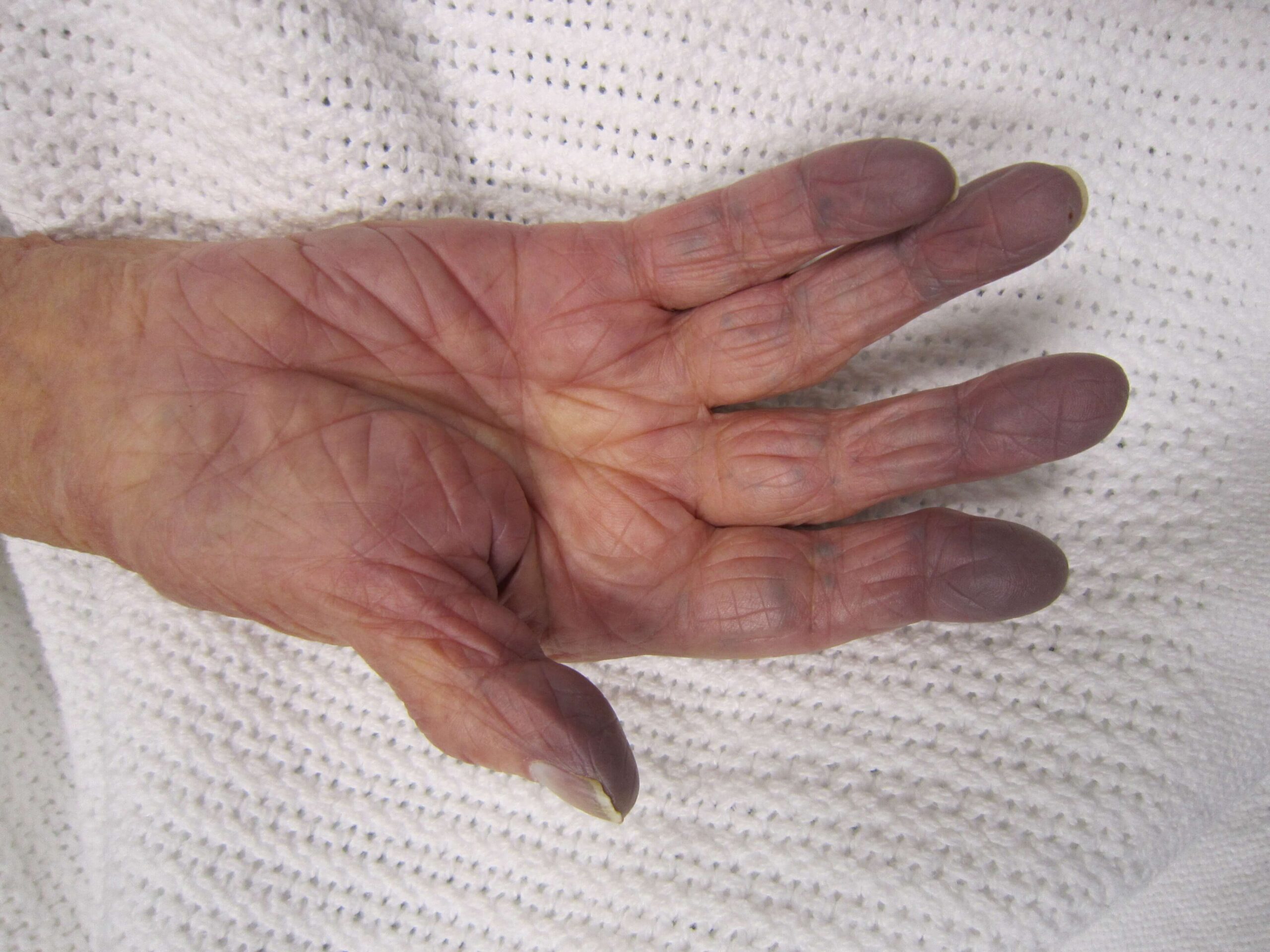
This change occurs when blood oxygen saturation reaches approximately 67%.
Low Blood Oxygen Levels Signs And Symptoms
Other than cyanosis and vision disorders, low blood oxygen levels can also result in abnormal circulation and may cause the following symptoms:
- Confusion
- Shortness of breath
- Headaches
- Restlessness
- Dizziness
- Rapid breathing
- Chest pain
- High blood pressure
- Lack of coordination
- Sense of euphoria
- Rapid heartbeat
- Slow heart rate
- Cough
- Wheezing
Hypoxemia, Hypoxia And Hyperoxia : Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
We humans, along with many other creatures on earth, require oxygen to stay alive.
Oxygen (O2) is life essential but as a drug has a maximum positive biological benefit and accompanying toxicity effects.
When we breathe, oxygen from the air enters our lungs and goes into our blood.
The oxygen then travels to all parts of the body through the blood.
It keeps our body healthy by letting the organs and tissues work normally.
When our body doesn’t have enough oxygen, our blood becomes darker.

In such cases, we could get hypoxemia or hypoxia ( low blood oxygen level ).
These are dangerous conditions.
Without oxygen, the brain, liver, and other organs can be damaged just minutes after the symptoms start.
You may find that hypoxia and hypoxemia have similar spellings; these two conditions are often confused.
While they can co-occur, they’re fairly different.
In short, hypoxemia refers to low oxygen content in the blood, whereas hypoxia means low oxygen supply in body tissues.
The two can sometimes, but not always, occur together.
In many cases, hypoxemia points to hypoxia.
This is because low oxygen concentrations in the blood often affect oxygen delivery to tissues.
Both hypoxemia or hypoxia also have similar symptoms, making the two even more difficult to discern.
On the other hand, when our body breathes oxygen at higher than normal partial pressure, we could get hyperoxia which can cause harm to the lung tissues.
The tiny air sacs also known as alveoli in the lung may fill with fluid or they may no longer inflate, causing a collapsed lung.
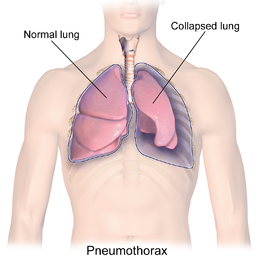
In this condition the lungs then can’t take in air normally and this makes it harder for the lungs to send oxygen into the blood.
Hyperoxia can lead to oxygen toxicity, which is also called oxygen poisoning.
It can cause coughing and trouble breathing.
In severe cases it can even cause death.
Causes Of Hypoxia
Hypoxia can occur in any condition, or event that reduces oxygen intake, and can reduce the amount of oxygen in body tissues, including:
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Low oxygen concentration in the surrounding air
- Carbon monoxide or cyanide
- Asthma attacks
- Lung diseases
- Heart diseases
Signs And Symptoms Of Hypoxia
The symptoms of hypoxia can vary based on the condition’s cause, and severity, including:
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Fast heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Headache
- Bluish color in the skin, lips, or fingernails (cyanosis).
Severe cases might even cause fainting or seizures.
In the case of low oxygen levels in the brain, a person might experience confusion, difficulty speaking, temporary memory loss, difficulty moving, or a coma.
Treatment For Hypoxia
The most common hypoxia treatment is oxygen therapy, which provides supplemental oxygen via a face mask or tubes placed in the nose or trachea.
In severe cases, mechanical ventilation might also be necessary.
To support heart function, a doctor might also give their patient intravenous fluids or medications to raise blood pressure or curb seizures, especially in cases that low oxygen in the brain.
Oxygen therapy usually uses compressed oxygen gas that is stored in a portable tank.
It will deliver oxygen to the patient’s body through nasal tubes, a face mask, or a tube inserted in the patient’s windpipe.
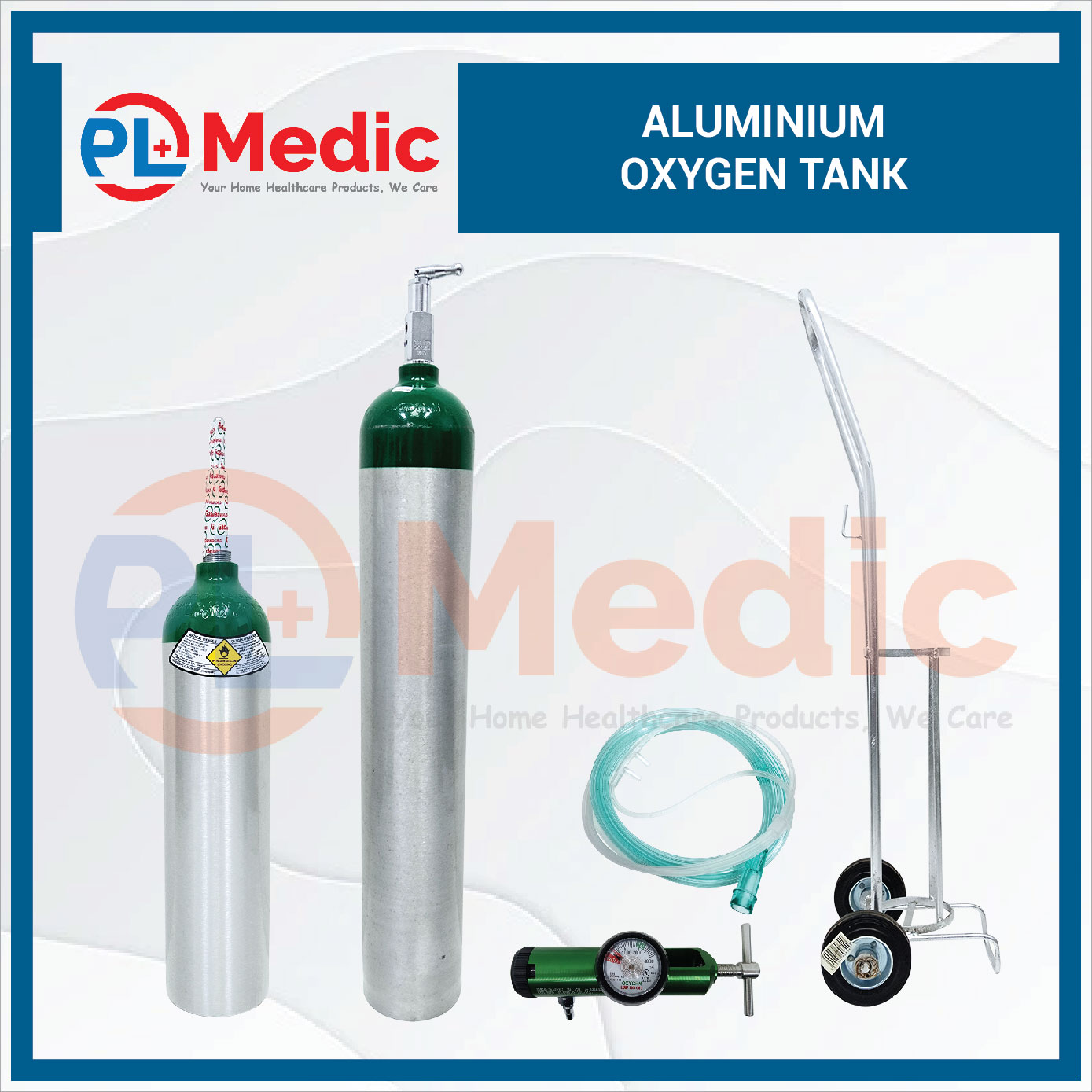

At PL Science Medic, we provide ready stock high quality Aluminium Oxygen Tank in affordable price with variations of 3 liter 0.4m3 and 5 liter 0.7m3.
Causes Of Hypoxemia
The underlying factors that can cause hypoxemia are relatively similar to those that cause hypoxia.
Due to this reason, the causes of hypoxemia and hypoxia can overlap.
Essentially, anything that reduces the ability to intake oxygen or oxygenate the blood can be a cause, including:
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) has been causing a life-threatening phenomenon called happy hypoxia but more precisely termed silent hypoxemia, in which a patient shows little to no symptoms but still has low blood oxygen levels.
- Asthma attacks
- Lung diseases
- Heart diseases
- Anemia
- High altitude
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) exacerbation — worsening of symptoms
- Emphysema
- Medications, such as certain narcotics and anesthetics, that depress breathing
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary edema (excess fluid in the lungs)
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in an artery in the lung)
- Pulmonary fibrosis (scarred and damaged lungs)
- Sleep apnea
Signs and Symptoms Of Hypoxemia
Since hypoxemia and hypoxia deal with the same condition of lack of oxygen, they have similar symptoms too, including:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Headache
- Fast heartbeat
- Confusion
- Sweating
- Bluish color in the skin, lips, or fingernails (cyanosis).
Severe cases can also cause hypoxemic respiratory failure, characterized by low blood oxygen levels but normal carbon dioxide levels.
Treatment For Hypoxemia
Similar to hypoxia, since hypoxemia involves low blood oxygen levels, the aim of treatment is to try to raise blood oxygen levels back to normal.
Oxygen therapy can be utilized to treat hypoxemia.
The process includes providing supplemental oxygen via a face mask or tubes placed in the nose or trachea.
Oxygen therapy is also available in concentrator form.
Unlike compressed oxygen, you don’t have to use prefilled oxygen containers.
Oxygen Concentrators are useful for people who need oxygen therapy all the time especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
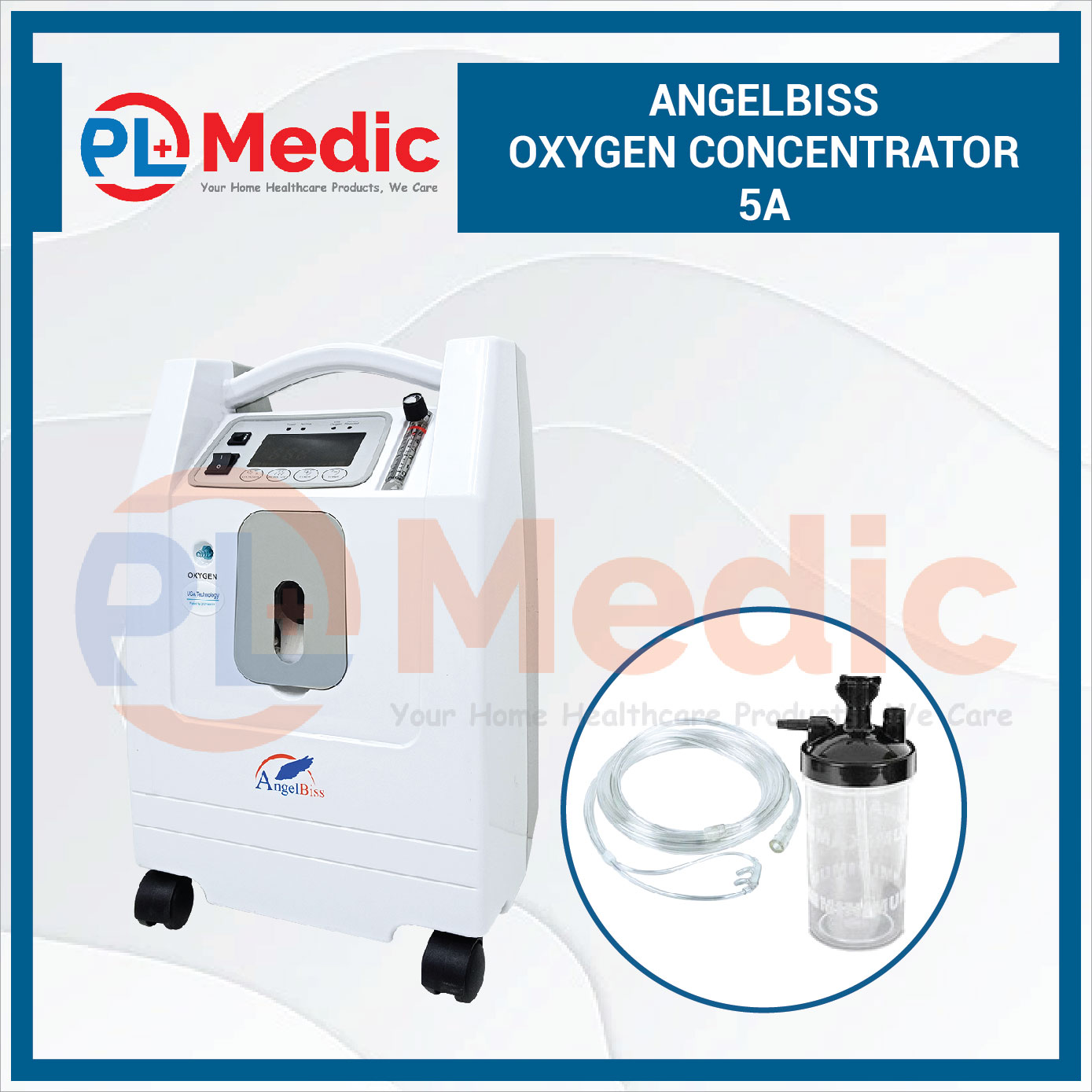
Take a look at PL Science Medic Angelbiss Oxygen Concentrator range from 5 liters to 10 liters airflow, preferred by medical professionals, pharmacies, and hospitals around Malaysia.
Causes Of Hyperoxia
Unlike hypoxemia and hypoxia that cause low blood oxygen levels, hyperoxia occurs when we are exposed to oxygen at partial pressures greater than those to which the body is normally exposed.
As the lung is exposed directly to the highest partial pressure of inspired oxygen, it is the primary target organ for oxygen-induced injury.
The causes of hyperoxia, including:
- Long-term use of supplemental oxygen
- Too deep or for too long when underwater diving with breathing apparatus
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Signs And Symptoms Of Hyperoxia
The symptoms of breathing high concentrations of oxygen for extended periods including:
- Coughing
- Mild throat irritation
- Chest pain
- Trouble breathing
- Muscle twitching in face and hands
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Nausea
- A feeling of unease
- Confusion
- Convulsions (seizure)
Treatment For Hyperoxia
Hyperoxia able to be managed by reducing exposure to increased oxygen levels.
In the case that have a collapsed lung.
The lungs may take weeks or more to recover fully on their own.
Thus, you may need to use a ventilator for a while.
A doctor may also release additional air around the lung by sucking it out through a needle.
This action allows the lung to fully expand.
Your medical professionals will tell you more about any other kinds of treatment.
How To Use An Oxygen Concentrator Correctly?
Around Malaysia, COVID-19 management has been seriously hampered by the inability of patients to find beds.
With hospitals being filled up to their capacity, patients are required to take care of themselves at home.
This also includes the use of oxygen therapy devices such as oxygen concentrators at home.
An oxygen concentrator uses the air to filter oxygen and is the best solution to oxygen supply at home.
Patients will access this oxygen through a mask or a cannula.
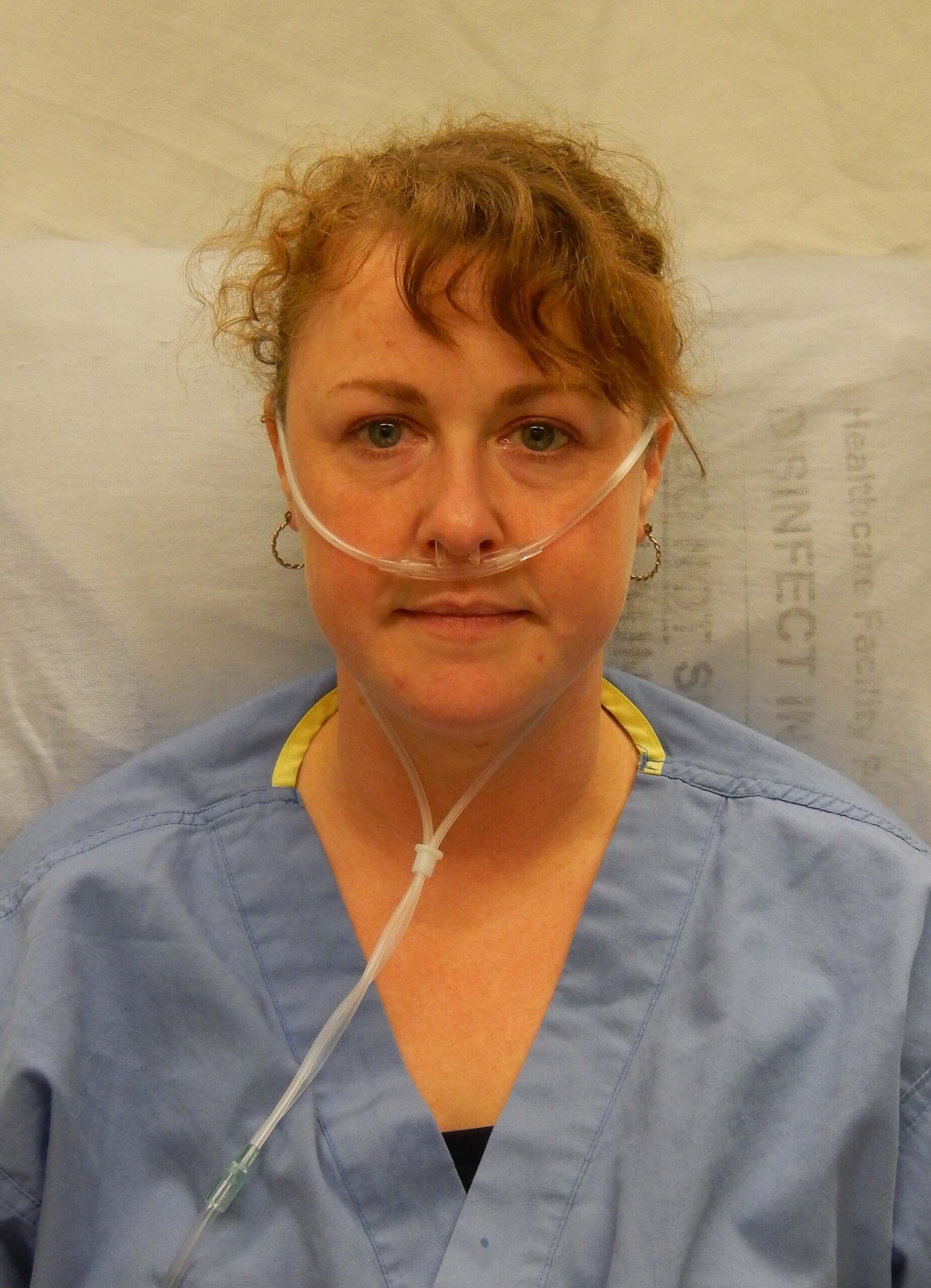
Oxygen concentrator generally used for patients with respiratory issues and with the ongoing crisis of COVID-19, can be very useful for patients whose oxygen levels drop.
One point to remember is that one should use a concentrator only when advised by a doctor.
Before using an oxygen concentrator, you can check your oxygen levels with a pulse oximeter.
If the pulse oximeter says that your SpO2 level or oxygen saturation is below 95 per cent, you may require supplemental oxygen.
A medical professional’s advice will provide more clarity on how long one should use oxygen supplement.
Lets take a look at how to setup your oxygen concentrator and use it correctly.
Setting Up Oxygen Concentrator
Before you use an oxygen concentrator, you need to setup the oxygen concentrator.
Remember to leave some space, don’t position the oxygen concentrator too close to the wall or furniture.
This is due to the oxygen concentrator need to pull in oxygen and release exhaust.
Make sure the area around it is unobstructed so that the oxygen concentrator gets enough space to circulate air.

Connect your humidification bottle if one is prescribed.
Check the manual that comes with the oxygen concentrator since the location of the outlet will vary depending on the model.
Always use distilled or filtered water in humidification bottle and change the water every time we use the machine.
Next, attach the oxygen tubing to the humidification bottle.
The oxygen concentrator has an air inlet filter that removes particles and allergens from the air.
Remove the filter from the oxygen concentrator once a week, wash it in warm water, squeeze out the excess water, and dry it with a clean towel to keep the filter clean.
Turning On Oxygen Concentrator
Start the oxygen concentrator at least 15-20 minutes before using it because it takes time to begin cycling the correct concentration of air.
Remember to follow the instructions based on the model or the directions provided by medical professionals.
Plug the oxygen concentrator into a grounded outlet.
The oxygen concentrator should be the only item plugged into that outlet, as it will draw a lot of power.
Better not use an extension cord, as this may cause a fire risk.

Switch on the power button and the lights will come on.
You’ll be able to hear the noise of air being pulled in and released.
The oxygen concentrator should sound an alarm for a few seconds when it’s turned on.
This is to make sure it’s not accidentally turned on when it’s not supposed to be.
The alarm will sound every time the oxygen concentrator is turned on.
If the power flow is interrupted the alarm will also sound.
After you finish using the oxygen concentrator, switch off the power button before plugging it up to prevent the oxygen concentrator get damaged.
Adjusting The Oxygen Flow Rate Of Oxygen Concentrator
Next, locate the liter control knob or switch that usually near the oxygen concentrator control panel.
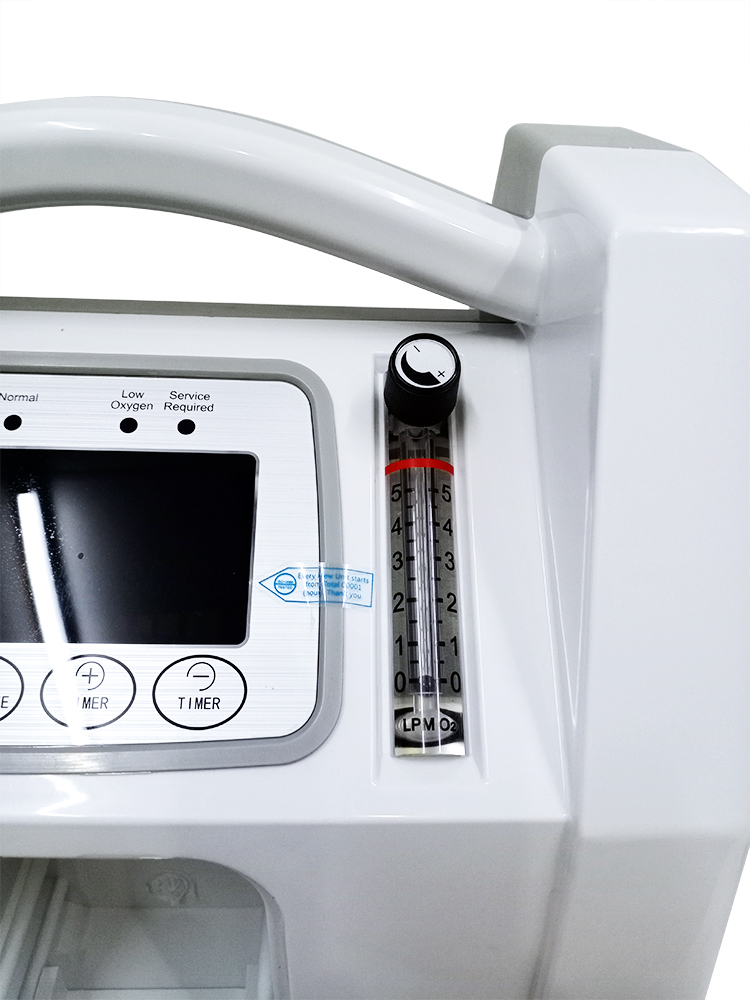
Double check the user manual to make sure using the right knob or switch.
Turn the knob or switch until it points to your prescribed number that is provided by your doctor or medical professionals.
If you aren’t sure about which setting to use, call the doctor for clarification.
It’s very important that you use the right amount of oxygen to avoid using more or less oxygen than the doctor has prescribed.
Using the wrong oxygen setting can be harmful, and may cause hypoxemia, hypoxia, or hyperoxia as mentioned before in this article.
If you think you’re not getting the right amount of oxygen, talk to your doctor about it.
Just remember don’t adjust your oxygen on your own.
Putting On The Nasal Cannula
You should check the tubing for any kinks or bends before putting it on.

These can interrupt the flow of oxygen, so smooth them out if you find any.
If there is a kink, you might not get all of the oxygen you need.
You may need to replace your tubing if it won’t straighten out.
Fit the nasal cannula upward into your nostrils for high levels of oxygen.
Each prong of the cannula should curve up into one nostril.
Once the prongs are in place, loop the tubes over your ears.
Adjust the tubes under your chin by sliding the tube adjuster up or down.
Use the oxygen concentrator for as long as your doctor recommends and switch the power off when the oxygen concentrator isn’t in use.
It’s important to not leave it running when it’s not in use to prevent it from overheating, causing a risk of fire.
Oxygen Level, Pulse Oximeter, Hypoxemia And COVID-19 Malaysia Conclusion
In this article we already discussed how COVID-19 lowers a person’s oxygen levels, low blood oxygen symptoms, and learn about devices such as pulse oximeters and oxygen concentrators.
I hope that this knowledge may be helpful to you.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a part of our daily lives nowadays in Malaysia.
But with about 3000 new cases a day in Malaysia, it remains as important as ever to stay vigilant and know how to protect yourself from coronavirus.

Are you using any medical devices to protect yourself from coronavirus?
Share your thoughts with us by commenting below.
Any comments, suggestions and corrections are most welcome.
Attention
Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with your personal healthcare professional or other medical professionals.
References
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_3
- https://www.houstonmethodist.org/blog/articles/2020/aug/
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/health-fitness/health-news/coronavirus-signs-of-low-oxygen-level-in-covid-19-patients/photostory/83136885.cms?picid=83136899
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2021.560592/full
- https://www.healthline.com/health/pulse-oximetry
- https://www.onhealth.com/content/1/normal_low_blood_oxygen
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperoxia
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/oxygen-saturation-914796
- https://www.singlecare.com/blog/hypoxia-vs-hypoxemia/
- https://www.webmd.com/asthma/guide/hypoxia-hypoxemia
- https://www.medicinenet.com/hypoxia_and_hypoxemia/article.htm
- https://myhealth.ucsd.edu/RelatedItems/3,90904
- https://www.wikihow.com/Use-an-Oxygen-Concentrator
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/hypoxemia/basics/causes/sym-20050930
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/oxygen-toxicity
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17727-hypoxemia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hypoxemia#hypoxia-vs-hypoxemia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/copd/hypoxia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/pulse-oximetry#purpose-and-uses
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/acl4222
- https://www.icmr.gov.in/pdf/covid/techdoc/